Product Description
Dry running rotary vane vacuum pumps, compressors and pressure-vacuum pumps
Introduction:
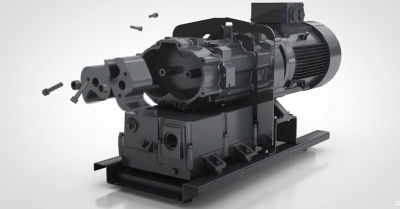
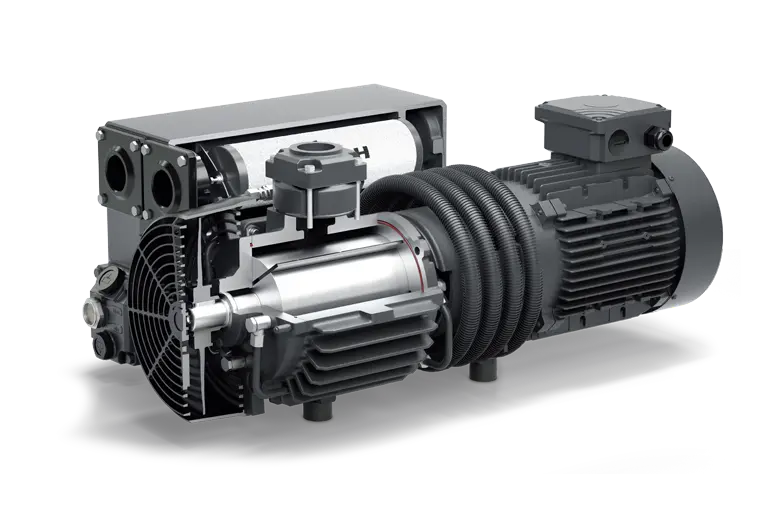
Rotary vane/pressure vacuum pumps,oil-free,air-cooled
The benefits of the new range are visible at a glance: maintenance and control panel are placed on 1 side only for easy access to filters and valves. Additional features include heat reduction through large cooling air pathways and vents. Design features such as the CHINAMFG ribs, optimised cooling air circulation, thermal separation of suction and compression chambers within the filter housing, as well as a minimum number of connected heat transferring parts reduce machine temperatures.
What is an oil-free vacuum pump?
An oil-free vacuum pump, also referred to an oil-less vacuum pump or dry running vacuum pump, is essentially a pump that does not use lubricants in the chamber to create a vacuum or cool the pump. In oil-lubricated machines lubrication is used a seal the vacuum chamber and cool the pump. Oil-free machines use other means to cool the machine during operation such as water or air cooling.
| Type | Suction air rate | Vacuum | Motor capacity(kw) | Speed | Noise Level | Weight | Overall dimensions | ||||||
| m3/h max. | Necessary | Install | (RPM) | dB(A) | kgs | mm | |||||||
| 50Hz | 60Hz | 50Hz | 60Hz | 50Hz | 60Hz | 50Hz | 60Hz | 50Hz | 60Hz | ||||
| ZYBW60E | 58 | 69 | 2.2 | 2.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 1420 | 1700 | 74 | 75 | 71 | 730*360*310 | |
| ZYBW80E | 70 | 82 | 2.9 | 3.8 | 4 | 4.8 | 1420 | 1700 | 75 | 76 | 72 | 730*360*310 | |
| ZYBW100E | 103 | 120 | 4 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 6.4 | 1420 | 1700 | 76 | 77 | 129 | 882*470*336 | |
| ZYBW140E | 137 | 160 | 5.8 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 9.3 | 1420 | 1700 | 77 | 78 | 140 | 884*470*336 | |
| Voltage 2.4-4.8Kw = 190-255/330-440V +5% 50Hz + 190-290/330-500V +5% 60Hz | |||||||||||||
| 5.5-9.3Kw = 340-430/588-745V +5% 50Hz + 340-500/590-865V +5% 60Hz | |||||||||||||
| a | b | b1 | d1 | d2 | d3 | e | e1 | e2 | f | g | g1 | |
| ZYBW60E | 326 | 190 | 95 | G 1″ | G 1″ | G 3/4 | 138 | 85 | 115 | 250 | 353 | 195 |
| ZYBW80E | 326 | 190 | 95 | G 1″ | G 1″ | G 3/4 | 138 | 85 | 115 | 250 | 353 | 195 |
| ZYBW100E | 398 | 245 | 123 | G 1 1/2″ | G 1 1/2″ | G 1 1/4″ | 190 | 95 | 155 | 295 | 470 | 223 |
| ZYBW140E | 398 | 245 | 123 | G 1 1/2″ | G 1 1/2″ | G 1 1/4″ | 190 | 95 | 155 | 295 | 470 | 223 |
| g2 | h1 | h3 | h4 | i | k | k1 | k2 | kM | kL | o | p | |
| ZYBW60E | 141 | 289 | 312 | 328 | 96 | 397 | 415 | 448 | 313 | 710 | 46 | 289 |
| ZYBW80E | 141 | 289 | 312 | 328 | 96 | 397 | 415 | 448 | 371 | 768 | 46 | 289 |
| ZYBW100E | 230 | 297 | 330 | 336 | 140 | 521 | 539 | 563 | 374 | 895 | 60 | 298 |
| ZYBW140E | 230 | 297 | 330 | 336 | 140 | 521 | 539 | 563 | 417 | 938 | 60 | 298 |
Typical applications are found in widely ranging sectors:
-
Printing and Paper
- Pre-Press
- Press
- Post-Press
- Central air supply
-
Woodworking
- Holding and lifting
- Preservation
- Wood drying
-
Textile
- Circular and flat knitting machines
- Draining and drying of dyed carpeting
- Fabric cutting tables
- Power air looms
- Sock knitting machines
- Steam treatment of yarn
-
Pneumatic Conveying
- goods in dust particle form (flour, cement)
- grain-type goods (dragées, granulate, pellets)
- piece goods (pneumatic tube conveying systems) and
- mixed goods.
-
Plastics
- Calibration
- Contact-free turning of plastic film
- Cooling and drying of extruded plastics
- Degassing extruders
- Degassing of rubber parts
- Dryers
- EPS-Foaming
- Generation of compressed air for plastic welding
- Pneumatic conveying systems
- Production of composite material
-
Parts Cleaning
- De-oiling under vacuum
- Dry-blasting
- Flood injection washing under vacuum
- Vacuum drying
-
Packaging
- Air cushion machines
- Blister packaging
- Filling and closing units
- Production of paper bags
- Reduction of transport volume
- Tray sealing
- Trim removal
-
Food and Beverage
- Bottle filling
- Chocolate production
- Cleaning of vegetables
- Coffee roasting
- Dairy processing
- Deaeration of mineral water
- Deodorizing of salad oils and fats
- Filtration units
- Fish and prawn pond aeration
- Food preservation
- Ham drying
- Humidification of tobacco
- Milking systems
- Meat processing and packaging
- Poultry processing
- Vacuum cutters
- Sterilizing
Why should you consider using an oil-free vacuum pump?
A low energy solution
Oil-free vacuum technologies offer considerable savings in terms of overall energy efficiency. Oil-free vacuum pumps when combined with a VSD (variable speed drive) can reduce energy consumption by up to 50% in some applications compared to their oil lubricated equivalents. The Specific Energy Requirement or SER is the ratio of the power consumption (in watts) of the vacuum pump to the respective pumping speed (m3/h) in relation to the suction pressure (mbar abs.). Simply stated, how much energy is needed to move a certain amount of air from A to B. The compression principles of oil-free vacuum pumps can allow for a much reduced SER depending on the application requirements. Most oil-free technologies are compatible with a VSD to allow for greater process accuracy from the pump and therefore reduce energy consumption further.
A clean solution
If you have a process that requires stringent or lower level of contamination risk then oil free vacuum pump offer an efficient and assured solution. These vacuum pumps have been specifically developed to meet the needs of manufacturers that require only the highest air purity environments.
A low maintenance solution
If you’re looking to reduce maintenance costs an oil-free vacuum pumps would be the ideal solution. These pumps do not require the same level of maintenance as an oil-lubricated machine. There is no need to replace the oil and separator elements, which is regularly required and naturally results in higher operating costs over the pump’s lifetime.
A low downtime solution
Unlike there oil lubricated counterparts, oil-free vacuum pumps do not have to be removed to carry out essential maintenance servicing. This means there is little or no equipment downtime, as well as any indirect costs from lost production uptime.
An environmentally friendly solution
Oil-free vacuum pumps remove the cost of lubricants, waste oil disposal and labour. They also have the additional benefit of reducing oil consumption in our manufacturing processes, lessening the user’s impact on the environment from production of oil and disposal of waste oil.
A lower total cost of ownership solution
All of the above benefits allow oil-free vacuum pumps to offer outstandingly low total cost of ownership (TCO) over the lifetime of the pump. Reduced service and maintenance costs, combined with energy savings will reduce operating costs per machine. Although the initial investment of an oil lubricated solution may look appealing, the lifetime costs far outweigh those of a dry running machine in the long-term.
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Kinetic Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Mainsuction Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Dry |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How Do You Maintain and Troubleshoot Vacuum Pumps?
Maintaining and troubleshooting vacuum pumps is essential to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Maintenance of Vacuum Pumps:
1. Regular Inspection: Perform regular visual inspections of the pump to check for any signs of damage, leaks, or abnormal wear. Inspect the motor, belts, couplings, and other components for proper alignment and condition.
2. Lubrication: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for lubrication. Some vacuum pumps require regular oil changes or lubrication of moving parts. Ensure that the correct type and amount of lubricant are used.
3. Oil Level Check: Monitor the oil level in oil-sealed pumps and maintain it within the recommended range. Add or replace oil as necessary, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
4. Filter Maintenance: Clean or replace filters regularly to prevent clogging and ensure proper airflow. Clogged filters can impair pump performance and increase energy consumption.
5. Cooling System: If the vacuum pump has a cooling system, inspect it regularly for cleanliness and proper functioning. Clean or replace cooling components as needed to prevent overheating.
6. Seals and Gaskets: Check the seals and gaskets for signs of wear or leakage. Replace any damaged or worn seals promptly to maintain airtightness.
7. Valve Maintenance: If the vacuum pump includes valves, inspect and clean them regularly to ensure proper operation and prevent blockages.
8. Vibration and Noise: Monitor the pump for excessive vibration or unusual noise, which may indicate misalignment, worn bearings, or other mechanical issues. Address these issues promptly to prevent further damage.
Troubleshooting Vacuum Pump Problems:
1. Insufficient Vacuum Level: If the pump is not achieving the desired vacuum level, check for leaks in the system, improper sealing, or worn-out seals. Inspect valves, connections, and seals for leaks and repair or replace as needed.
2. Poor Performance: If the pump is not providing adequate performance, check for clogged filters, insufficient lubrication, or worn-out components. Clean or replace filters, ensure proper lubrication, and replace worn parts as necessary.
3. Overheating: If the pump is overheating, check the cooling system for blockages or insufficient airflow. Clean or replace cooling components and ensure proper ventilation around the pump.
4. Excessive Noise or Vibration: Excessive noise or vibration may indicate misalignment, worn bearings, or other mechanical issues. Inspect and repair or replace damaged or worn parts. Ensure proper alignment and balance of rotating components.
5. Motor Issues: If the pump motor fails to start or operates erratically, check the power supply, electrical connections, and motor components. Test the motor using appropriate electrical testing equipment and consult an electrician or motor specialist if necessary.
6. Excessive Oil Consumption: If the pump is consuming oil at a high rate, check for leaks or other issues that may be causing oil loss. Inspect seals, gaskets, and connections for leaks and repair as needed.
7. Abnormal Odors: Unusual odors, such as a burning smell, may indicate overheating or other mechanical problems. Address the issue promptly and consult a technician if necessary.
8. Manufacturer Guidelines: Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance and troubleshooting specific to your vacuum pump model. Follow the prescribed maintenance schedule and seek professional assistance when needed.
By following proper maintenance procedures and promptly addressing any troubleshooting issues, you can ensure the reliable operation and longevity of your vacuum pump.
What Is the Role of Vacuum Pumps in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing?
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various aspects of pharmaceutical manufacturing. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes to support a range of critical operations. Some of the key roles of vacuum pumps in pharmaceutical manufacturing include:
1. Drying and Evaporation: Vacuum pumps are employed in drying and evaporation processes within the pharmaceutical industry. They facilitate the removal of moisture or solvents from pharmaceutical products or intermediates. Vacuum drying chambers or evaporators utilize vacuum pumps to create low-pressure conditions, which lower the boiling points of liquids, allowing them to evaporate at lower temperatures. By applying vacuum, moisture or solvents can be efficiently removed from substances such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), granules, powders, or coatings, ensuring the desired product quality and stability.
2. Filtration and Filtrate Recovery: Vacuum pumps are used in filtration processes for the separation of solid-liquid mixtures. Vacuum filtration systems typically employ a filter medium, such as filter paper or membranes, to retain solids while allowing the liquid portion to pass through. By applying vacuum to the filtration apparatus, the liquid is drawn through the filter medium, leaving behind the solids. Vacuum pumps facilitate efficient filtration, speeding up the process and improving product quality. Additionally, vacuum pumps can aid in filtrate recovery by collecting and transferring the filtrate for further processing or reuse.
3. Distillation and Purification: Vacuum pumps are essential in distillation and purification processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Distillation involves the separation of liquid mixtures based on their different boiling points. By creating a vacuum environment, vacuum pumps lower the boiling points of the components, allowing them to vaporize and separate more easily. This enables efficient separation and purification of pharmaceutical compounds, including the removal of impurities or the isolation of specific components. Vacuum pumps are utilized in various distillation setups, such as rotary evaporators or thin film evaporators, to achieve precise control over the distillation conditions.
4. Freeze Drying (Lyophilization): Vacuum pumps are integral to the freeze drying process, also known as lyophilization. Lyophilization is a dehydration technique that involves the removal of water or solvents from pharmaceutical products while preserving their structure and integrity. Vacuum pumps create a low-pressure environment in freeze drying chambers, allowing the frozen product to undergo sublimation. During sublimation, the frozen water or solvent directly transitions from the solid phase to the vapor phase, bypassing the liquid phase. Vacuum pumps facilitate efficient and controlled sublimation, leading to the production of stable, shelf-stable pharmaceutical products with extended shelf life.
5. Tablet and Capsule Manufacturing: Vacuum pumps are utilized in tablet and capsule manufacturing processes. They are involved in the creation of vacuum within tablet presses or capsule filling machines. By applying vacuum, the air is removed from the die cavity or capsule cavity, allowing for the precise filling of powders or granules. Vacuum pumps contribute to the production of uniform and well-formed tablets or capsules by ensuring accurate dosing and minimizing air entrapment, which can affect the final product quality.
6. Sterilization and Decontamination: Vacuum pumps are employed in sterilization and decontamination processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Autoclaves and sterilizers utilize vacuum pumps to create a vacuum environment before introducing steam or chemical sterilants. By removing air or gases from the chamber, vacuum pumps assist in achieving effective sterilization or decontamination by enhancing the penetration and distribution of sterilants. Vacuum pumps also aid in the removal of sterilants and residues after the sterilization process is complete.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, dry screw pumps, or liquid ring pumps, may be utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing depending on the specific requirements of the process and the compatibility with pharmaceutical products.
In summary, vacuum pumps play a vital role in various stages of pharmaceutical manufacturing, including drying and evaporation, filtration and filtrate recovery, distillation and purification, freeze drying (lyophilization), tablet and capsule manufacturing, as well as sterilization and decontamination. By enabling efficient and controlled processes, vacuum pumps contribute to the production of high-quality pharmaceutical products, ensuring the desired characteristics, stability, and safety.
What Industries Commonly Rely on Vacuum Pump Technology?
Vacuum pump technology finds applications in various industries where creating and controlling vacuum or low-pressure environments is crucial. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Manufacturing and Production: Vacuum pumps are extensively used in manufacturing and production processes across multiple industries. They are employed for tasks such as vacuum molding, vacuum packaging, vacuum degassing, vacuum drying, and vacuum distillation. Industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and food processing rely on vacuum pump technology to achieve precise and controlled manufacturing conditions.
2. Chemical and Pharmaceutical: The chemical and pharmaceutical industries heavily rely on vacuum pumps for numerous applications. These include solvent recovery, vacuum filtration, vacuum drying, distillation, crystallization, and evaporation. Vacuum pumps enable these industries to carry out critical processes under reduced pressure, ensuring efficient separation, purification, and synthesis of various chemical compounds and pharmaceutical products.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics: The semiconductor and electronics industries extensively use vacuum pumps for manufacturing microchips, electronic components, and electronic devices. Vacuum pumps are crucial in processes such as physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapor deposition (CVD), etching, ion implantation, and sputtering. These processes require controlled vacuum conditions to ensure precise deposition, surface modification, and contamination-free manufacturing.
4. Research and Development: Vacuum pump technology is integral to research and development activities across scientific disciplines. It supports experiments and investigations in fields such as physics, chemistry, materials science, biology, and environmental science. Vacuum pumps facilitate processes like freeze drying, vacuum distillation, vacuum evaporation, vacuum spectroscopy, and creating controlled atmospheric conditions for studying various phenomena.
5. Food and Beverage: The food and beverage industry relies on vacuum pumps for packaging and preservation purposes. Vacuum sealing is used to extend the shelf life of food products by removing air and creating a vacuum-sealed environment that inhibits spoilage and maintains freshness. Vacuum pumps are also used in processes like freeze drying, vacuum concentration, and vacuum cooling.
6. Oil and Gas: In the oil and gas industry, vacuum pumps play a role in various applications. They are used for crude oil vacuum distillation, vacuum drying, vapor recovery, gas compression, and gas stripping processes. Vacuum pumps help maintain optimal conditions during oil refining, gas processing, and petrochemical manufacturing.
7. Environmental and Waste Management: Vacuum pumps are employed in environmental and waste management applications. They are used for tasks such as soil vapor extraction, groundwater remediation, landfill gas recovery, and wastewater treatment. Vacuum pumps facilitate the removal and containment of gases, vapors, and pollutants, contributing to environmental protection and sustainable waste management.
8. Medical and Healthcare: The medical and healthcare sectors utilize vacuum pumps for various purposes. They are used in medical equipment such as vacuum-assisted wound therapy devices, vacuum-based laboratory analyzers, and vacuum suction systems in hospitals and clinics. Vacuum pumps are also used in medical research, pharmaceutical production, and medical device manufacturing.
9. Power Generation: Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation industries, including nuclear power plants and thermal power plants. They are used for steam condensation, turbine blade cooling, vacuum drying during transformer manufacturing, and vacuum systems for testing and maintenance of power plant equipment.
10. HVAC and Refrigeration: The HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries rely on vacuum pumps for system installation, maintenance, and repair. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate air and moisture from refrigerant lines and HVAC systems, ensuring optimal system performance and efficiency.
These are just a few examples of industries that commonly rely on vacuum pump technology. The versatility and wide-ranging applications of vacuum pumps make them indispensable tools across numerous sectors, enabling precise control over vacuum conditions, efficient manufacturing processes, and scientific investigations.


editor by CX 2023-11-17